Speaker
Description
Highlight of this work: This work predicts the optimal coil phasing, semi-empirical threshold coil current and ‘favorable’ $q_{95}$ window for ELM mitigation for HL-2M 1MA discharge scenario. It is found that pressure gradient may play an important role on determining the peeling-tearing displacement near X-point, due to the curvature effect (GGJ effect) of equilibrium magnetic field.
Resonant magnetic perturbation (RMP) generated by external coils is an effective method to suppress or mitigate edge localized mode (ELM) in H-mode toroidal plasma. Extensive efforts have been devoted to understand the mechanism of controlling ELM. It is demonstrated that edge-peeling response to RMP fields plays an essential role. The linear single fluid model (employed in MARS-F code) predicted results are in good agreement with experiential measurements in many cases $[1]$. MARS-F is widely applied to interpret the experimental observations and to optimize of RMP coil configuration.
This work focuses on the optimization of coil phasing for ELM control for the coming HL-2M tokamak device and on the influence of pressure profile at pedestal region on RMP fields, using MARS-F code. In the computations, plasma rotation and plasma resistivity are included. The former induces the screening of the applied RMP fields, while the latter yields the penetration of field. Moreover, the strong parallel sound wave damping term is also included, which moderately damps the core-kink response. The resonant radial perturbed magnetic field component b$^1_{res}$ at plasma edge or the plasma displacement ($\xi_X$) near the X-point is taken as the indicator to optimize coil phasing here. Actually, these two criteria are basically equivalent $[2]$.
We consider a equilibrium of HL-2M with 1.0 MA current. The key parameters are: major radius $R_0=1.75$ m, minor radius $a=0.65$ m, $B_T=1.8$ T, $q_0=1.07$, $q_{95}=3.25$ and plasma normalized pressure $\beta_N=1.63$ being much smaller than the no wall beta limit ($\beta^{no-wall-limit}_N \ \sim 3.6$). There will be two off-midplane rows of coils. Each row includes 8 coils, which allows the configurations with the maximum toroidal harmonic being $n=1, 2$ and $4$.
For HL-2M, the coil basic parameters were already determined, such as the the coil width ($\Delta \theta =15^o$) and radial location ($\theta_c=\pm 40^o$). However, the off-midplane coils have one degree of freedom to choose : the coil phasing $\Delta \Phi$. The current on upper and lower coils is simply expressed as $I_{upper}\propto cos(n\phi)$ and $I_{lower}\propto cos(n\phi+\Delta\Phi)$, respectively. The numerical results indicate that the optimal coil phasing for n=1, 2 and 4 are $\Delta\Phi_{opt}=\pm 180^o , 100^o$ and $-50^o$, respectively. At the optimal phasing $\Delta\Phi_{opt}$, the edge-peeling response is dominant over the so-called core-kink response $[3]$. The maximum of $\xi_X$ for n=1 is about 1.5 and 10 times larger that of n=2 and 4, respectively. While the optimal phasing is not sensitive to the choose of toroidal rotation profile and pressure profile. During the variation of pressure profile, the normalized beta $\beta_N$ and q profile are fixed. More interesting, it is found that the amplitude of $\xi_X$ is generally reduced when the pressure gradient at edge increases. This is likely due to that the pressure gradient (GGJ effect) makes kink-tearing mode more stable. It is implied that the required minimum coil current for suppressing/mitigating ELM is enhanced when plasma pressure profile becomes more sharp at edge.
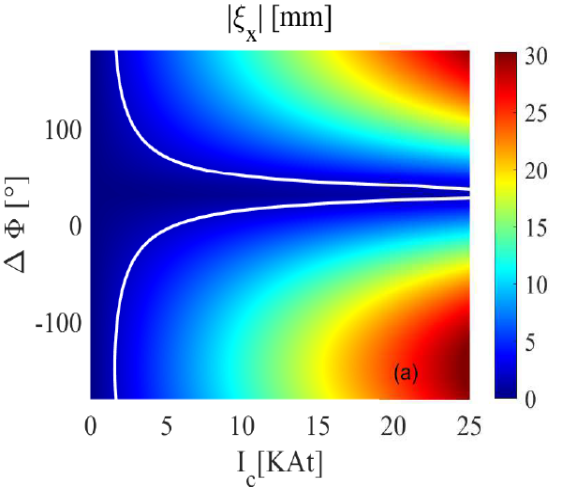
The comparison between linear response modeling and experiments in MAST $[4]$ yields a critical X-point displacement $\xi_X\sim 1.5 $ mm for achieving ELM mitigation. We simply assume the critical value $\xi_X\sim 2 $ mm as the guideline for controlling ELM on HL-2M, although there are difference in plasma configuration, coil geometry, and the actual threshold coil current between these two machines. In fig.1, the solid white curves represent the 2 mm level of X-point displacement. Clearly, at the designed coil geometry ( $\Delta \theta=15^o$ , $\theta_c=\pm 40^o$ ), the required coil current depends on the choice of coil phasing. With the bad choice of coil phasing (e.g. $0<\Delta \Phi<\sim 50^o$ ), the required coil current exceeds the the allowed maximum RMP coil current (=10 kAt) as designed. On the other hand, there is a wide region of ‘good’ coil phasing, which needs $I_c< 5$ kAt for achieving ELM mitigation based on the 2 mm X-point displacement criterion. Similar study will be carried out for other toroidal mode number.
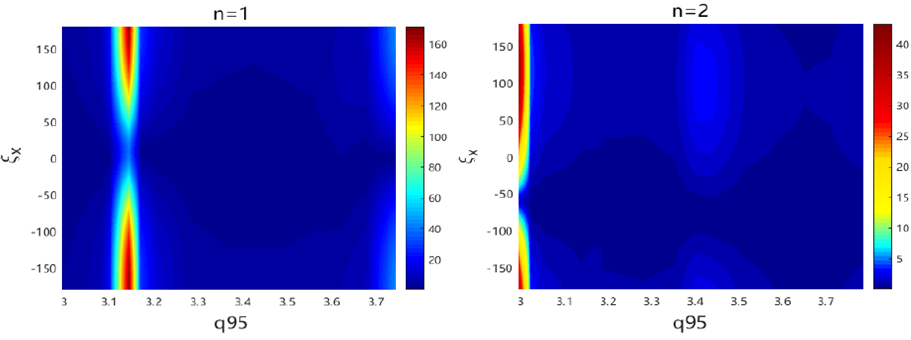
Usually, the ELM mitigation/suppression is sensitive the $q_{95}$ value $[1]$. We predict the effective $q_{95}$ window for HL-2M as shown in fig.2. For $n=1$ case, the most effective $q_{95}$ window is in 3.1<$q_{95}$<3.2, in which the maximum (e.g. at the optimal coil phasing) of b$^1_{res}$ amplitude is about 8 times larger than that outside of this window. For $n=2$ case, the best window exists near $q_{95}~3$. Another ‘favorable’ $q_{95}$ window is 3.4<$q_{95}$<3.5. It is noted that the optimal coil phasing is not sensitive to the variation of $q_{95}$ for the studied equilibrium. Here, during scan of $q_{95}$, $\beta_N=1.63$ is fixed.
References
$[1]$ Y.Q. Liu, et.al, Phy. Plasmas 24, 056111, (2017);
$[2]$ L.N. Zhou et al. Nucl. Fusion, 58,076025, (2018);
$[3]$ Y.Q.Liu et.al. Nucl. Fusion 51, 083002, (2011);
$[4]$ A. Kirk et al. Nucl. Fusion, 55,043011, (2015)
| Affiliation | Southwestern Institute of Physics, China |
|---|---|
| Country or International Organization | China |
